Macular Degeneration Explained: Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Latest Treatment Options
Introduction to Macular Degeneration
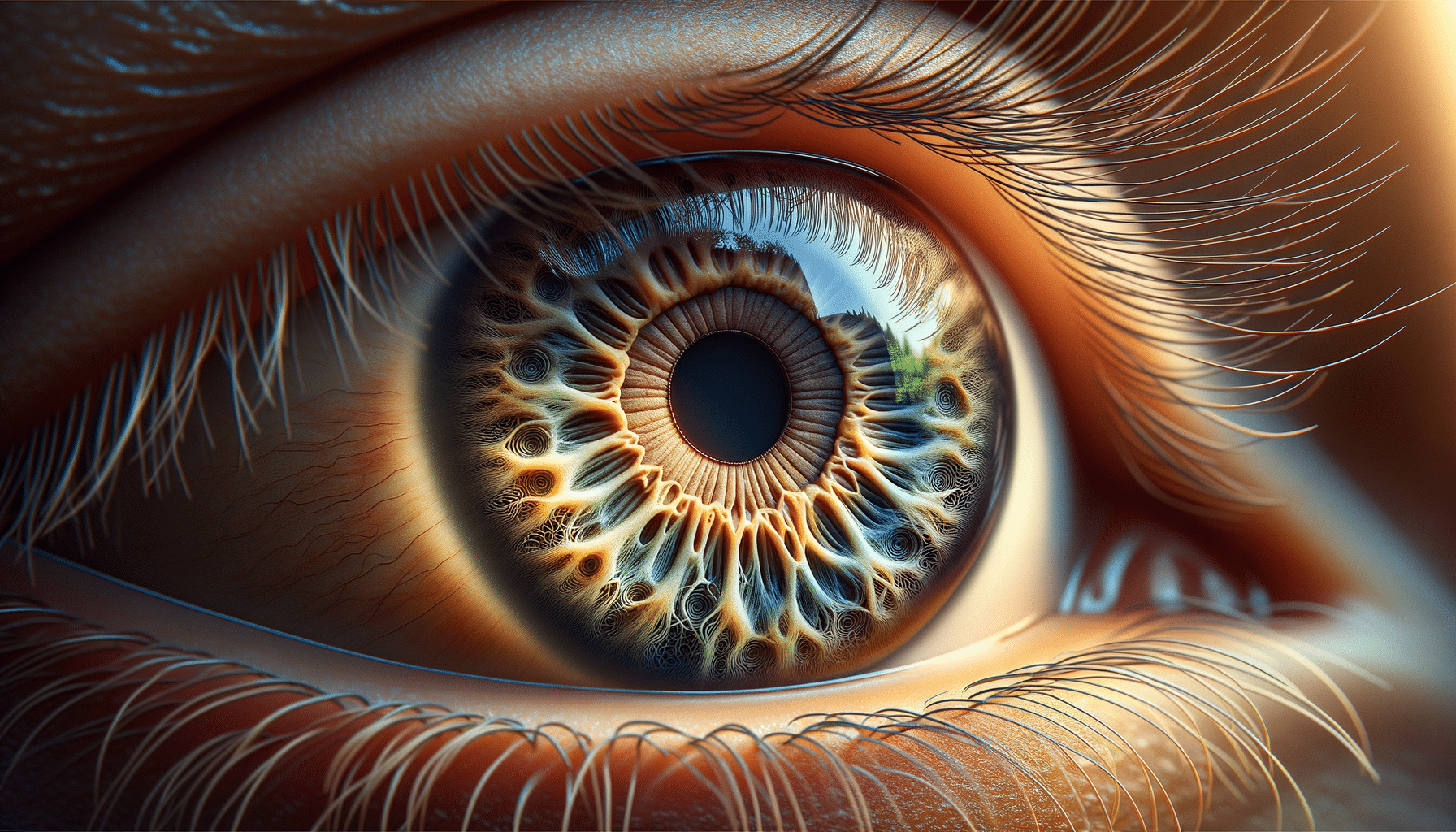
Macular Degeneration is a condition that primarily affects the central part of the retina, known as the macula. This area is responsible for sharp central vision, which is crucial for activities such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces. As one of the leading causes of vision loss, understanding macular degeneration is essential for early detection and management. Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is the most common form, typically affecting individuals over 50. The condition can significantly impact quality of life, making awareness and education vital components in combating its effects.
Types and Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
There are two primary types of AMD: dry and wet. The dry form is more common and progresses slowly, while the wet form is less common but can lead to rapid vision loss. Symptoms often start with blurred vision, difficulty seeing in low light, and a diminished ability to perceive colors. In advanced stages, AMD can cause a central blind spot, making everyday tasks increasingly challenging. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to more effective management and better outcomes.
It is important to note that while AMD does not cause complete blindness, it severely impairs central vision, which is critical for detailed tasks. Regular eye examinations are crucial, especially for those with a family history of the condition. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can slow the progression of vision loss.
Risk Factors Associated with Macular Degeneration
Understanding the risk factors associated with AMD can help in taking preventive measures. Age is the most significant risk factor, with the likelihood of developing AMD increasing after the age of 50. Family history and genetics also play a crucial role, as the condition tends to run in families. Lifestyle choices such as smoking and poor diet can further elevate the risk. Smoking, in particular, is known to double the risk of AMD, making cessation a vital preventive strategy.
Other factors include obesity, high blood pressure, and prolonged exposure to sunlight. A diet rich in green leafy vegetables, fish, and antioxidants can help reduce risk. Regular eye exams and a healthy lifestyle are key components in preventing or delaying the onset of AMD.
Latest Treatment Options for Macular Degeneration
While there is no cure for AMD, several treatment options can slow its progression and improve quality of life. For dry AMD, supplements with antioxidants and zinc have shown promise in slowing vision loss. For wet AMD, treatments include anti-VEGF injections, which help reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. These injections can stabilize vision and, in some cases, improve it.
Emerging treatments such as retinal implants and gene therapy are also being explored. These innovative approaches aim to restore some degree of vision or halt the disease’s progression. Staying informed about the latest advancements and maintaining regular consultations with eye care professionals can help manage AMD effectively.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Vision
Macular Degeneration poses a significant threat to central vision, but with early detection and appropriate management, its impact can be minimized. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and available treatments empowers individuals to take proactive steps in preserving their vision. Regular eye check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and staying updated on medical advancements are crucial in the fight against AMD. Protecting your vision is not just about preserving sight, but also about maintaining independence and quality of life.